Tag: 5G
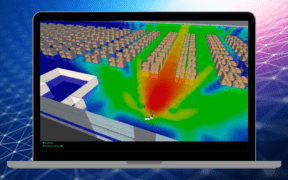
The design prediction accuracy report is one of many reports featured in iBwave Design, a leading RF planning and design tool for indoor wireless systems. This report compares RF coverage prediction versus measured data at a venue. In this blog, we’ll explain what the numbers in the report mean, how they should be interpreted, and […]

While enterprises have predominantly relied on public networks in the past, that situation has changed with the 5G shift in private networks. Private networks, principally 4G/LTE, have become much more common, offering numerous advantages over public networks, including: However, there is a shift happening in the market and more 5G deployments are taking place, driven […]

Private 5G networks and dedicated cellular networks are not new. But they hit a critical turning point in 2022, with 100s or perhaps even over 1,000 deployments for a variety of applications on in enterprise communications on enterprise campuses, industrial sites, as well as local fixed-wireless use. All this activity shows that deployments are beginning […]
