5G vs. Multiple Network Technologies: Enterprise Connectivity Dilemma
Share

In the ever-evolving landscape of connectivity solutions, enterprises face a pivotal decision – whether to embrace the promise of 5G or deploy a blend of multiple network technologies. While the allure of a 5G-centric future is undeniable, practical considerations and real-world complexities necessitate a more nuanced approach. This article delves into the key factors that influence the choice between deploying 5G and integrating multiple network technologies, exploring use cases, considerations, and future trends.
The Complex Reality of Enterprise Connectivity
The widespread anticipation surrounding 5G’s transformative potential is undeniable. However, the practical reality is far more intricate. Enterprises operate within a realm where a myriad of connectivity solutions coexist, each catering to unique demands. Wi-Fi, IoT-dedicated systems, Bluetooth, and others are evolving alongside 5G, presenting a diverse ecosystem of options.
The notion of a 5G “monoculture” is compelling, but it clashes with a host of commercial, technical, and regulatory constraints. These constraints encompass legacy systems that perform well, lack of suitable 5G devices for IoT, frequency band limitations, higher costs, certification requirements, skill shortages, geopolitical restrictions, and more. These realities necessitate a thorough evaluation of when to deploy 5G and when to blend it with other technologies.
Suitable Scenarios for Enterprise 5G Deployments
Deploying 5G can be suitable for the following applications:
- High-Speed Connectivity Applications: In scenarios where ultra-fast data speeds and low latency are critical, like industrial automation, real-time analytics, and immersive AR/VR applications.
- Massive IoT Deployments: When deploying a massive number of IoT devices that require 5G’s enhanced capacity and support for a high density of connections.
- Mission-Critical Applications: For applications demanding robust and reliable connectivity, such as remote surgery, autonomous vehicles, and emergency response systems.
- Unreachable Locations: When extending wired connectivity is impractical, 5G can provide a cost-effective solution to connect remote or underserved areas.
- Future-Proofing: Choosing 5G as a long-term investment to accommodate future applications and services that demand higher data rates and network capabilities.
- Enhancing Campus-Wide Coverage: Deploying 5G across a large campus or facility to provide comprehensive coverage for various use cases and devices.
- Next-Generation Entertainment: For entertainment venues seeking to provide high-quality streaming, gaming, and interactive experiences to visitors.
Keep in mind to conduct a thorough assessment of specific use cases and technical requirements before opting for a 5G-only deployment. To learn more, read our article about the importance of Deploying Private 5G for Enterprises!
Key Use-Case Scenarios for Multiple Networks
The integration of multiple network technologies offers a strategic advantage in various scenarios:
- Separate Networks for Specific Environments: Enterprises may opt for separate networks indoors and outdoors or for on-site and off-site roaming. This separation caters to distinct connectivity needs within different environments.
- Device-Led Network Integration: Certain devices are inherently tied to specific networks. A worker on a production line, for instance, may use Wi-Fi for a connected tool while wearing a 5G-connected headset for guidance. This scenario emphasizes the need to integrate networks based on device capabilities.
- Migration Strategy: Transitioning from legacy networks to new infrastructures is a gradual process. Enterprises may need to run old and new networks in parallel to ensure smooth migration without disrupting operations.
- Backup and Resilience: Multi-network integration enhances resilience against cyber threats, software bugs, and emergencies. Critical systems can switch between networks in the event of failures, ensuring continuity of operations.
- Backhaul and Gateway Scenarios: Employing one wireless technology for backhaul to another’s access points optimizes cost and performance. Satellite backhauls, mmWave radios, and Wi-Fi meshes illustrate this strategy.
- Bonded and Hybrid Networks: Combining diverse 4G/5G radios, public and private networks, and other technologies offers increased coverage, throughput, and efficiency. This approach is particularly relevant for applications like vehicle fleets, public safety agencies, and large campuses.
- Shared Infrastructure and Tools: Enterprises can share physical infrastructure, network design tools, operations centers, and security platforms across multiple networks, fostering efficiency and collaboration.
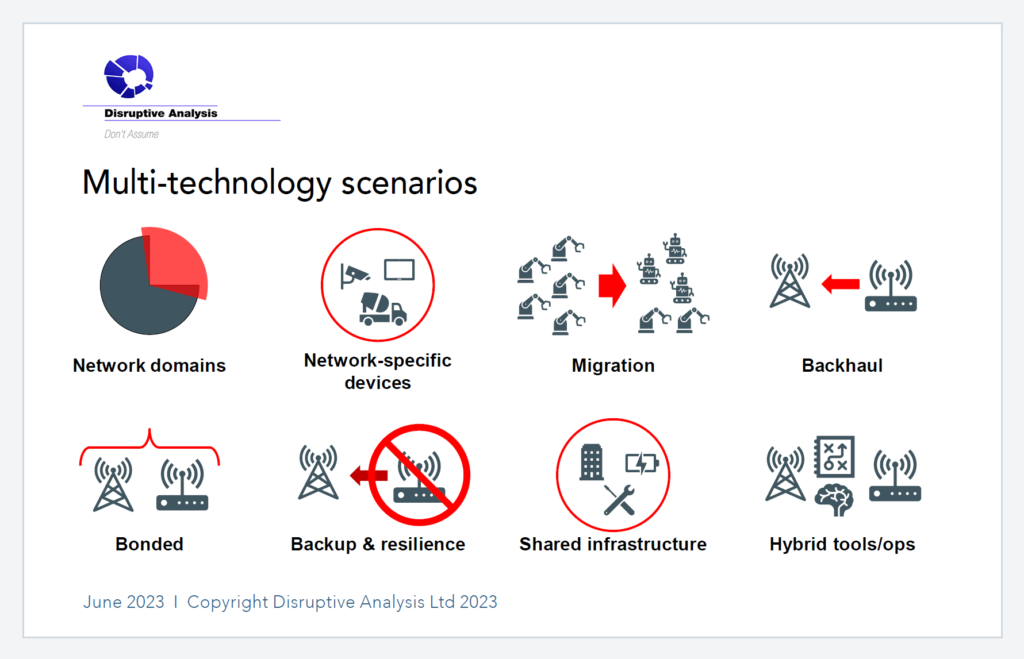
Source: Disruptive Analysis
The Real-World Example: Airports
To illustrate the practical application of these concepts, consider an airport. Airports extensively use wireless networks for passenger Wi-Fi, service vehicles, air-traffic control, and more. While these networks largely operate independently, specific scenarios demand integration.
For instance, a private 5G network can serve service vehicles on the ramp, while public 4G/5G covers broader areas. Wi-Fi might bridge indoor and outdoor networks for seamless coverage. This example underscores the complexity of integrating networks based on diverse use cases.
Examples of Wireless Network Combinations
Consider the microcosm of an airport, where diverse networks serve different purposes. From passenger Wi-Fi to air-traffic control, each network often stands alone. Yet, scenarios arise where blending two platforms is vital, leaving room for expansion.
Prominent network combinations include:
In the current landscape, common combinations include:
Private 4G + Private 5G: Many sites begin with LTE for private networks, often transitioning to 5G for advanced use cases. Others adapt from early “non-standalone” 5G networks, combining the technologies for enhanced capabilities. For instance, manufacturing plants blend private 4G for equipment monitoring with private 5G for real-time operations.
Private 5G + Public 4G/5G: Common for users traversing localized and wide-area networks. Field workers in utilities travel between private sites and public networks, using dual-SIM devices for seamless connectivity. Airports use private networks for better indoor coverage while bridging to public networks for broader access.
Private 5G + Wi-Fi: Vital hybrid combination with various technical approaches. Private 4G/5G backhauls enhance outdoor Wi-Fi access points. In-building Wi-Fi bridges to outdoor private 5G, for instance, connecting warehouse operations. Entertainment venues utilize Wi-Fi for visitors and private 5G for critical functions like payment terminals.
Private 4G/5G + PMR: Industrial sectors adapt legacy private-radio systems with private 4G/5G for smoother transitions. Airports deploy private 4G/5G networks for ground staff while relying on older radios for baggage handlers. Utility field workers use private radios for maintenance and private 5G at newer facilities.
Various hybrid wireless scenarios emerge:
Countless other permutations exist, like private 5G with satellite or Wi-Fi combined with Bluetooth Low Energy for smart buildings. Yet, network complexity extends beyond technology integration, encompassing security, device management, and more. Commercial and HR considerations underline the need for astute integrator and service provider choices.
Private 5G + Satellite: Industries in remote areas benefit from this blend, such as shipping companies or oil/mining exploration ventures.
Wi-Fi + Bluetooth Low Energy: Smart buildings leverage Wi-Fi for well-powered equipment and Bluetooth Low Energy for battery-operated sensors.
Private Cellular + LoRa: Large enterprise sites can integrate high data-rate users with low-power/low-volume IoT endpoints, enhancing connectivity and efficiency.
Source: Disruptive Analysis
Navigating Future Trends
As we peer into the future, several trends will shape the landscape of network technologies:
Private 5G’s Evolution: Private 5G networks will mature further, transitioning from trial deployments to production networks. Cloud-based network-as-a-service models will simplify deployments.
Use-Case Stacking: Businesses will expand 5G usage within existing industry verticals, extending initial deployments to accommodate additional applications or coverage areas.
5G Evolution and New Features: 5G will continue to evolve with new features and releases. Releases 17 and 18 will introduce precise positioning, ultra-low latency, and low-power IoT connectivity, expanding 5G’s capabilities.
Innovation Across Technologies: Wi-Fi will advance with spectrum expansion and new features. Satellite networking will gain prominence, linked to 5G through non-terrestrial networks. Specialist service providers and system integrators will play a crucial role in delivering 5G solutions.
Glimpses of 6G: Early discussions about 6G are underway, but its commercial viability for enterprises is distant. 5G’s impact will remain dominant until around 2030, with early trials and testbeds exploring future use cases.
Designing 5G and Multi-Technology Networks
The process of designing and integrating multiple networks, including the seamless incorporation of 5G, is a complex undertaking that demands meticulous planning and execution. Design considerations encompass coverage, capacity, network architecture, device compatibility, and more. The challenge lies in harmonizing diverse technologies into a cohesive framework that optimizes performance and meets operational needs. This intricate process calls for expert guidance and innovative tools to ensure successful implementation.
Here, iBwave takes center stage, offering a comprehensive suite of wireless network design solutions. Whether it’s optimizing private 5G deployment, integrating Wi-Fi with 5G for seamless coverage, or incorporating satellite connectivity into the network mix, iBwave provides the tools and expertise needed to design multi-technology networks with precision. By leveraging iBwave’s advanced capabilities, businesses can confidently navigate the complexities of 5G and multi-network integration. iBwave’s seamless survey and design solutions enable enterprises to weave together the threads of connectivity, ensuring reliability, efficiency, and a future-ready network infrastructure that paves the way for innovation and success.
You can leverage the capabilities of iBwave Private Networks for designing Private LTE, 5G and Wi-Fi seamlessly in one solution. You can also use our flagship solution iBwave Design for designing wireless networks for any type of inbuilding environment and network or iBwave Reach if you’re interested in designing indoor/outdoor campus networks. Whatever your network needs are, iBwave has you covered. Learn more about our solutions here!
Conclusion
In the intricate world of enterprise connectivity, the decision to deploy 5G or integrate multiple network technologies is far from straightforward. Balancing technical feasibility, financial considerations, legacy systems, and future-proofing requires a holistic perspective. As the technological landscape continues to evolve, enterprises must carefully assess use cases, select integrators wisely, and adapt to the dynamic interplay between 5G and other wireless solutions. By embracing a flexible and strategic approach, businesses can navigate the complexities and carve a path toward a connected future that maximizes efficiency and innovation.
If you want to learn about 5G use cases and integrate multiple network technologies, read our eBook!

- The Role of Private Wireless Networks in the Energy Industry - August 1, 2024
- How to Streamline Building Modeling in Network Design - January 8, 2024
- 5G vs. Multiple Network Technologies: Enterprise Connectivity Dilemma - August 18, 2023


















Great article!
Thank you for your comment. We’re glad you liked our article. Please stay tuned for our upcoming blogs!
A complete and illustrative comparison between 5G and other technologies. Thanks for sharing.
Thank you. We appreciate your comment. Please stay tuned for our upcoming blogs!